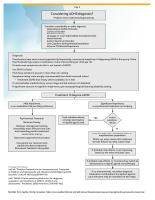
Introduction and Overview
The following resources are widely used in clinical settings to screen and assess, design treatment protocol, prescribe medication and provide referrals for children and adolescents with symptoms of ADHD.
Screening & Assessment
A guide to designing treatment protocol for a patient with ADHD symptoms.
Psychological assessment tool for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder symptoms that includes a teacher rating scale, parent rating scale, and scoring scale.
Treatment
Evidence-Based Treatments for ADHD
- Therapist Aid offers several clinical tools for managing ADHD (worksheets, skill packets, study tips, etc.)
- Behavioral Therapies: There are many different types of behavioral therapies than can help to support youth with ADHD. Behavioral therapies often focus on how to encourage children to try new behaviors, reward desired behaviors, or “extinguish” maladaptive behaviors (Society of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 2020).
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): A common therapy for individuals with ADHD. CBT is a type of talk therapy focusing on how thoughts and emotions affect behavior.
Referral and Co-Management
NA for this topic
Medications (Non-Stimulant)
Atomoxetine (Strattera)
- Comes in: 10, 18, 25, 40, 60, 80, 100 mg
- Start at: 0.5 kg (1 to 1.2 mg/kg/d usual full dosage)
- Titration schedule to effect:
- Most common dose range: Max Daily Dose: 100 mg
- FDA
Clonidine (Catapres)
- Comes in: 0.1, 0.2, 0.3 mg
- Start at: 0.5 mg QHS if <45 kg, otherwise 0.1 mg QHS (Caution if <5 yr.)
- Titration schedule to effect:
- Most common dose range: Max daily dose 27-49 kg 0.2 mg, 40-45 kg 0.3 mg >45 kg 0.4 mg
- FDA
Clonidine XR (Kapvay)
- Comes in: 0.1, 0.2 mg
- Start at: 0.1 mg QHS
- Titration schedule to effect:
- Most common dose range: Max daily dose 0.4 mg
- FDA
Guanfacine (Tenex)
- Comes in: 1, 2 mg
- Start at: 0.5 mg QHS if <45 kg, otherwise 1 mg QHS (Caution if <5 yr.)
- Titration schedule to effect:
- Most common dose range: Max daily dose 27-49 kg 2 mg, 40-45 kg 3 mg >45 kg 4 mg
- FDA
Guanfacine XR (Intuniv)
- Comes in: 1, 2, 3, 4 mg
- Start at: 1 mg QD if over 6 years old (full dosage 0.05 to 0.12 mg/kg
- Titration schedule to effect:
- Most common dose range: Max daily dose Whichever is lower: 4mg/day 6-12 years old, 7mg/day 13-17 years old or, 0.05-0.12 mg/kg/day
- FDA
Medications (Stimulant)
Metadate ER
- Comes in: 10, 20 mg tab
- Start at: 10 mg QAM
- Titration schedule to effect:
- Most common dose range: Max Daily Dose: 60 mg
- FDA
Concerta
- Comes in: 18, 27, 36, 54 mg
- Start at: 18 mg QAM
- Titration schedule to effect:
- Most common dose range: Max Daily Dose: 72 mg
- FDA
Adderall XR
- Comes in: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30 mg
- Start at: 5 mg QD
- Titration schedule to effect:
- Most common dose range: Max Daily Dose: 30 mg
- FDA
Metadate CD (30% IR)
- Comes in: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, mg capsules
- Start at: 10 mg QAM
- Titration schedule to effect:
- Most common dose range: Max Daily Dose: 60 mg
- FDA
Ritalin LA (50% IR)
- Comes in: 10, 20, 30, 40, mg capsules
- Start at: 10 mg QAM
- Titration schedule to effect:
- Most common dose range: Max Daily Dose: 60 mg
- FDA
Focalin XR
- Comes in: 5 to 40 mg 5 mg steps
- Start at: 5 mg QAM
- Titration schedule to effect:
- Most common dose range: Max Daily Dose: 30 mg
- FDA
Daytrana patch
- Comes in: 10, 15, 20, 30 mg capsules
- Start at: 10 mg QAM
- Titration schedule to effect:
- Most common dose range: Max Daily Dose: 30 mg
- FDA
Lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanse)
- Comes in: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70 mg capsules
- Start at: 30 mg QD
- Titration schedule to effect:
- Most common dose range: Max Daily Dose: 70 mg
- FDA
Dexedrine Spansule
- Comes in: 5, 10, 15 mg capsules
- Start at: 5 mg QAM
- Titration schedule to effect:
- Most common dose range: Max Daily Dose: 40 mg
- FDA
Quilivant XR
- Comes in: 25 mg/5 ml 1 bottle = 300 mg or60 ml
- Start at: 10 mg QAM
- Titration schedule to effect:
- Most common dose range: Max Daily Dose: 60 mg
- FDA
Quilicew ER
- Comes in: 20, 30, 40 mg capsules
- Start at: 20 mg QAM
- Titration schedule to effect:
- Most common dose range: Max Daily Dose: 60 mg
- FDA
Billing/Coding
96160
- Can code two per visit
- Code pays $7.91 (at well visit and at E+M visit)
- Examples: Bright Futures Adolescent Supplemental Questionnaire, GAPS, HEADSSS
96127
- Can code two per visit
- Code pays $4.10 (at well visit and at E+M visit)
- Examples: PSC, SCARED, CDI, CES-DEC, PHQ-9 Modified for Adolescents, Vanderbilt, Conners
99408
- May be reported in addition to E/M or Health Check
- Code pays $30.73 (only code if screen is positive & counseling is documented from 3-15 minutes)
- Examples: CRAFFT for Substance Use/Abuse
Additional Resources for Families
Websites
- Parents Med Guide: Quality information about medications for ADHD.
- Children and Adults with ADHD (CHADD): Offers information, support groups, training and other resources for professionals and caregivers.
Podcasts
- ADHD 365 Podcast: Children and Adults with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (CHADDD)
- ADHD Smarter Parenting Podcast
Apps
- Breathe, Think, Do with Sesame: App to teach child skills such as problem solving, self-control, planning, and task persistence.
Fact Sheets
- NAMI (ADHD)
- Understanding ADHD: Information for Parents About Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
- NIH: The Basics
- ADHD Info Packet: Support for families of children with disabilities
Articles
- How ADHD Can Affect Your Family: Source WebMD
- Understanding ADHD: Information for parents from Healthy Children
Books
Books families may find helpful
- Taking Charge of ADHD: The Complete Authoritative Guide for Parents (Revised Edition, 2000), by Russell A. Barkley, PhD
- Raising Resilient Children: Fostering Strength, Hope and Optimism in Your Child (2002), by Robert Brooks, PhD and Sam Goldstein, PhD Attention Deficit Disorder: The Unfocused Mind in Children and Adults (2006), by Tom Brown, PhD
- Teenagers with ADD and ADHD: A Guide for Parents and Professionals (2006), by Chris Dendy
Books children may find helpful:
- Learning to Slow Down & Pay Attention: A Book for Kids about ADHD (2004), by Kathleen Nadeau, PhD, Ellen Dixon, PhD, and Charles Beyl
- Jumpin’ Johnny Get Back to Work! A Child’s Guide to ADHD/Hyperactivity (1981), by Michael Gordon, PhD
Videos
- Childhood ADHD: What are the signs and symptoms?